What about more detail
on Aspirin atom economy
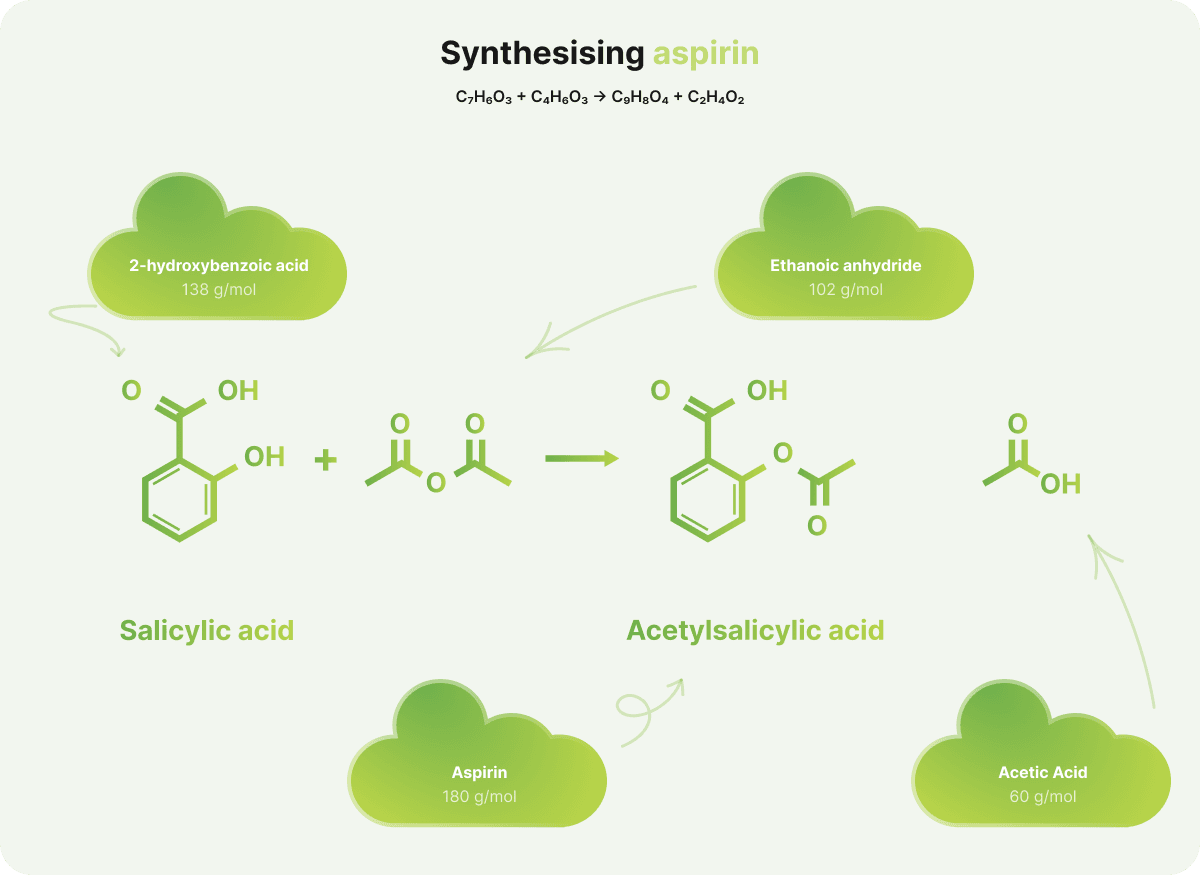
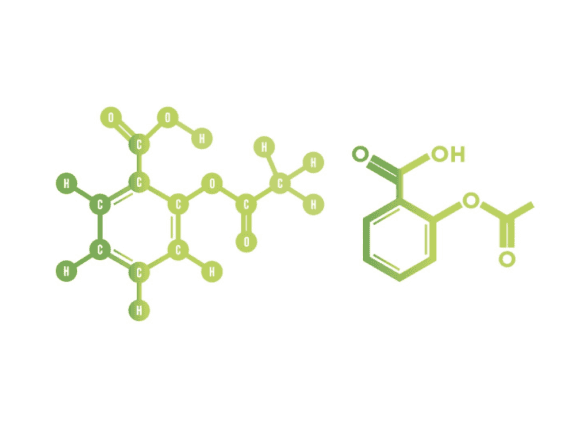
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid, has a molar mass (Mr) of 180.17 g/mol. Below is a simplified overview of how atom economy is calculated for its synthesis.

What about more detail
on Aspirin atom economy
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid, has a molar mass (Mr) of 180.17 g/mol. Below is a simplified overview of how atom economy is calculated for its synthesis.